Whether it is a physical store or an e-commerce business, SEO has become a necessity for digital branding and marketing alike. Marketers focus on various metrics, including content optimization, keyword analysis, and getting valuable backlinks to improve SEO value. Average Page Load Time (or simply Load Time) is one metric which remained relatively neglected until recently.
The evolution of smartphones changed the way marketers looked at Load Time. Being data-conscious, mobile users need access to fast and light web content. This is what gave rise to Accelerated Mobile Pages (aka Google AMP).
Regarded as the best way to have a completely integrated internet experience, Google AMP is an open-source initiative backed by Google. It allows you to design mobile-friendly pages that load instantly on all mobile devices. But, the question most marketers have in mind is: “Will it affect my SEO? If so, how?”
In this post, we will learn in detail about Google AMP, as well as its impact on content and SEO.
1. What Is Google AMP?
The fundamental principle behind creating AMP is to offer a lightweight and easy-to-load version of your website. It is a reliable, mobile-data-friendly, and faster alternative to mobile optimization where all elements including pictures, videos, and JavaScript files load properly each time the website is viewed.
Here is how a regular web page and an AMP web page look.
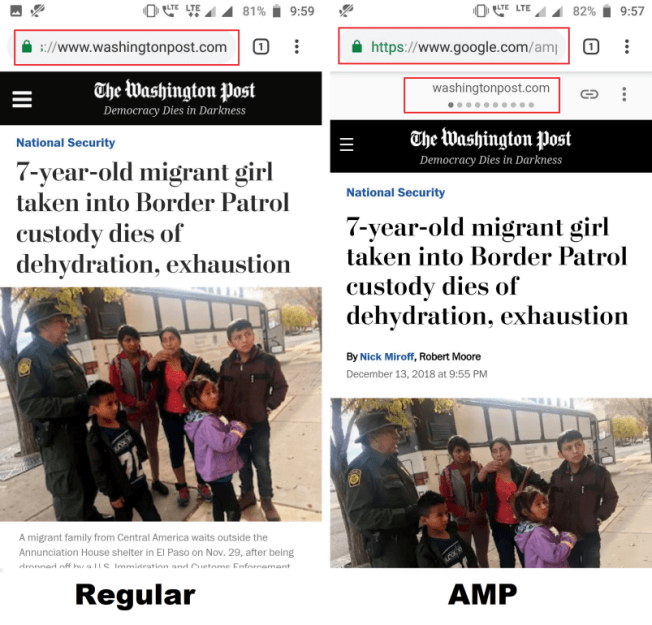
AMP uses elemental or basic HTML. JavaScript speeds up the loading time. In addition to this, Google caches the pages to reduce upload time. In other words, AMP is stripped down to a simple form of code that removes all unnecessary elements to create fast and lightweight web pages. The pages that are “AMP-ed” will be tagged (a white lightning bolt in a gray circle).
AMP loads content before images and advertisements. Google also hosts a cut down version of your website on its servers to increase loading speed. Google officially integrated AMP listings into its mobile search results on February 24th, 2016.
2. How Does It Work?
Instant web page loading is at the heart of AMP. The three primary elements that help make this happen include AMP HTML, AMP JS library, and Google AMP Cache.
A. AMP HTML
This revamps the current HTML of a page to incorporate custom AMP properties. Some of the HTML tags are replaced with suitable AMP components. These restrictions for putting together rich web content render AMP HTML the exact speed it needs to load pages instantly.
B. AMP JS (JavaScript)
The AMP JavaScript library is exclusively designed for mobile pages. It loads all external resources in controlled portions. Thus, servers don’t have to fetch multiple commands at once, preventing the chances of overloading, and thereby slowing down the web pages. AMP pages can also pre-calculate the layout of all elements on a page, disable slow CSS selectors, and sandbox all iframes to improve loading speed.
C. Google’s AMP Cache
Google’s AMP Cache is a proxy-based delivery network responsible for distributing all valid AMP documents. Its primary function is to transmit and then cache the AMP pages, which can automatically improve their performance over time.
These three factors help AMP render web content as quickly as possible.
But, how does this affect your SEO? Let’s see.
3. How Will Google AMP affect SEO?
AMP is not a direct search engine factor; not using AMP won’t affect your website or the content on it. However, it comes with different benefits – which will ultimately have an impact on your SEO efforts.
A. The Benefits of AMPs
- Increased Speed
Naturally, the greatest advantage of AMP is improved speed, which is one of the critical SEO metrics. Higher speed means visitors are less likely to lose patience and navigate away from your web page. That, in turn, improves your engagement rate, resulting in a higher SEO ranking.
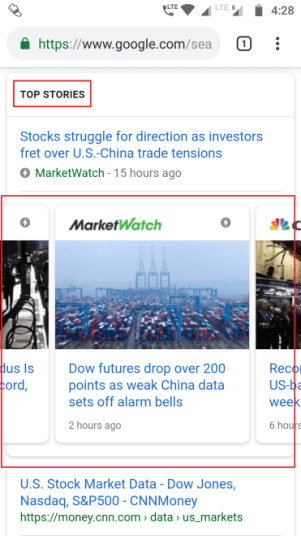
- Increased Visibility in Carousel
We are not talking about the carnival carousel here. Google has reserved a special place for AMP web pages in the “Top Stories” carousel above all other search engine results in SERPs.

Although the carousel mostly showcases trending news and topics, you can create an AMP on trending subjects to secure a place above SERPs. Plus, Google has also started showing AMP-ed web pages in organic search results.
- Higher Dwell Time
For mobile visitors, quick loading time often translates to longer dwell time. The minimalist design of the AMP encourages users to spend more time on an AMP-ed web page. It is easier for visitors to navigate through the content as there are no distractions. Plus, the text is mobile-optimized, making it easy to read.
- Lower Bounce Rates
Bounce rate is a critical SEO factor. One of the reasons behind a high bounce rate is, you guessed it, slow loading speed. Nearly 53% of mobile site visits leave a page that takes longer than three seconds to load. However, AMP web pages load quickly, resulting in better user engagement, which in turn, can bring this metric down to a more friendly number.
B. The Drawbacks of AMPs
- JavaScript & CSS Limitations
As AMP uses modified versions of HTML and has CSS restrictions, you have to avoid using flashy elements when possible. The usage of JavaScript is also highly restricted – as you can only use special AMP elements, leaving no room for customized JavaScript.
In other words, you can’t use special functions like transitions, pop-ups, hidden content, and social media. As a result, you may not be able to create a style that reflects your brand to the fullest extent.
- Reduced On-Site Tracking
As Google stores AMPs as caches on its server, there is little support for script tags. So, for the time being, the analytics available for AMPs leave much to be desired. If you want to explore Google Analytics fully, AMP may not be your best option. However, you can bet that marketers will eventually find solutions for this.
- Lack of Control
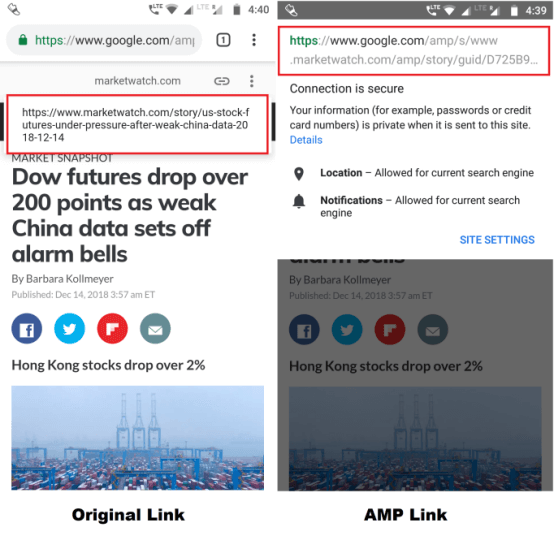
Storing AMPs on Google’s server is necessary for faster loading speeds. Whenever an AMP page loads, the original website link is replaced by https://google.com/amp/yourpageURL. This means Google provides the search results served in the AMPs. This means you are not directly serving the content, even though you created it.
However, Google now lets you view and share original links in AMP pages, following some backlash from publishers for stealing their web traffic.
- Difficult to Implement Lastly, being a new technology, AMP is not the easiest thing in the world to incorporate. Fortunately, there are a few awesome WordPress AMP plugins. These AMP-integration tools can automatically add AMP functionality to your WordPress site. However, they often lead to conflicts with SEO tools such as Yoast. Generally speaking, you probably need to have professional developer experience (or hire someone who does) to resolve implementation-related issues.
4. Who Uses Google AMP?
Despite its few drawbacks, AMP has been steadily gaining popularity. Online publishers and news sites have found AMP most helpful – as they are primarily used to broadcasting trending news and topics.
Plus, news publishers adopting AMP also get a coveted place in publisher carousels in mobile SERPs. With AMP pages, Wired Magazine witnessed a 25% rise in average click-through rates and a 63% increase in click-through rates on ads in AMP stories.
However, e-commerce sites are also experimenting with AMP. For example, on June 30, 2016, eBay started its AMP-powered mobile shopping experience. The online retailer made nearly 8 million AMP-based browse nodes available in production. eBay was one of the first few online stores to start using AMP.
Another successful example is how much health brand Zespri increased their web traffic with Google Amp.
5. Should You Be Using Google AMP?
Implementing AMP requires a considerable investment. So, before adopting AMP, you need to carefully consider the following points:
- What is your market niche? Do you serve B2B consumers or B2C prospects?
- Who are your online prospects? Do they use mobile phones to consume web content? If your consumers are baby boomers or senior citizens, they are less likely to use smartphones. So, using AMP might not be 100% ideal in this scenario.
- Is your website already mobile-optimized? Does it load quickly on all mobile devices? If your site is already loading quickly, you might not need to use AMP.
Do you publish content regularly? Do you have a blog that weaves trending topics into new posts? In such a case, your business can benefit from AMP technology. If you publish evergreen content, however, using AMP will be a waste of time and resources.
Parting Words
With mobile becoming increasingly prevalent, it’s a safe assumption that you will need to use AMP eventually. It will also evolve over time and hopefully include features, such as direct links to the original website. One thing is clear though, whenever you decide to use AMP, it will have a positive impact on your SEO if implemented carefully.
If you are still unsure of taking the AMP route, talk to us at Ayokay. We can help you decide if it is the best choice and provide you with all the resources needed to make the most of AMP web pages.
Jack Shepler is a Marketing and Search Engine Optimization expert. He founded Ayokay, award-winning marketing, and web design firm in Indianapolis, Indiana that has built brands, increased sales for businesses, and helped nonprofit organizations fulfill their missions since 2011. He uses his decades of experience to educate through the Ayokay blog and through public speaking. You can follow him on LinkedIn.